- Home /
- Documentation
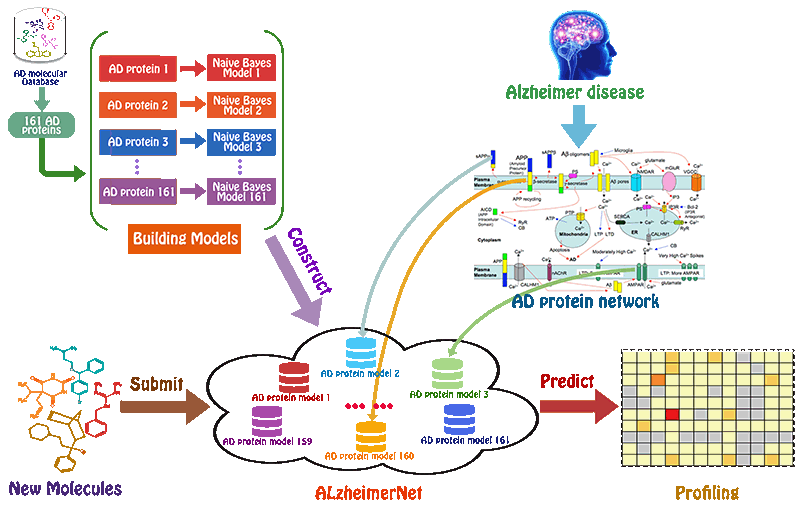
Preparation of the chemicals and AD-related proteins
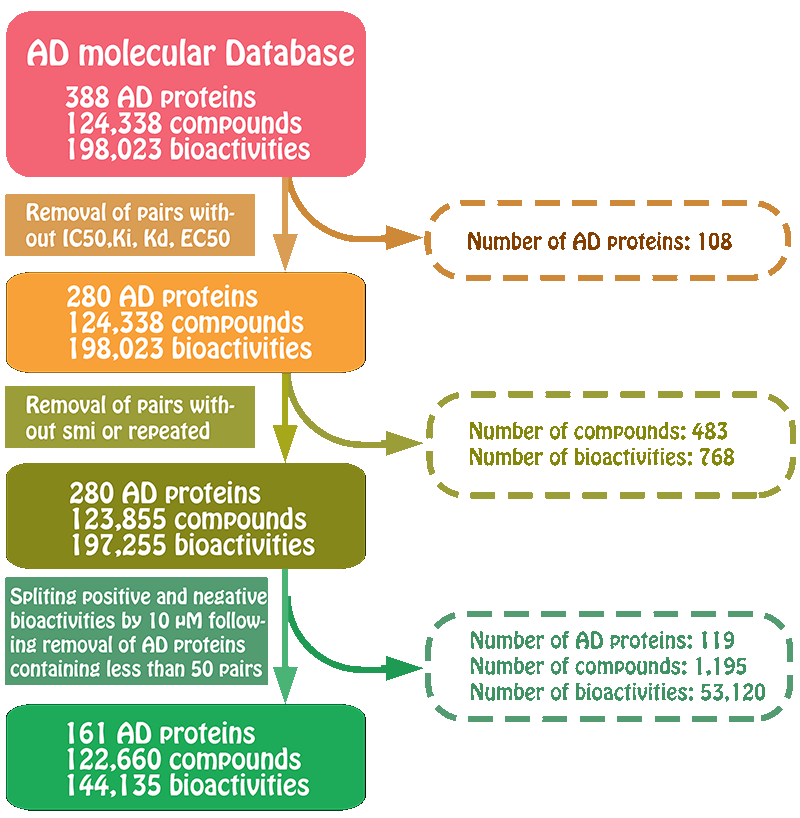
We used BindingDB database as our training datasets. BindingDB is a public, web-accessible database of measured binding affinities, focusing chiefly on the interactions of proteins considered to be candidate drug-targets with ligands that are small, drug-like molecules. For AD-related proteins, activity data were filtered to keep only activity end-point points that had half-maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50), half-maximum effective concentration (EC50) or Ki values. Herein, to ensure that enough number of molecules could be used in model building, we previously selected those targets with larger than 200 biological activity data. Following this procedure, 109061 compounds associated with 161 AD-related proteins remained with 115257 activity end-points, which were used for model building.
Preparation of the positive and negative set
For those compounds with more than one activity values, we took the mean value of their activity values as the final activity value. A compound was considered active when the mean activity value was below 10 uM. All compounds higher than 10 uM are considered inactive. Following this split, maybe some AD-related proteins have very little number of negative samples. To balance the number between positive samples and negative samples for each AD-related protein, we randomly selected certain number of compounds from other AD-related proteins to generate the negative samples for these AD-related proteins. The number of these selected negative samples together with inactive samples should be basically equal to the number of the active samples for these AD-related proteins. These prepared positive set and negative set were used as the subsequent model building.
Model training and validation
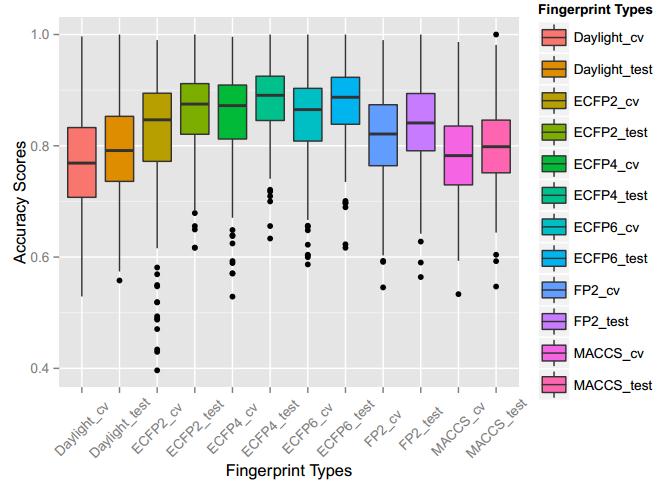
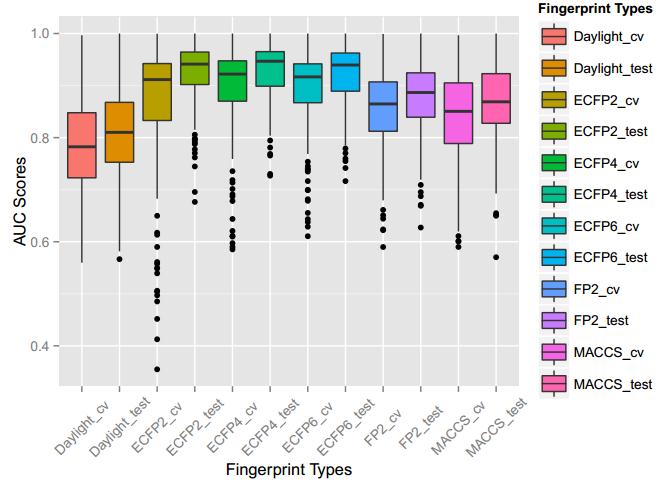
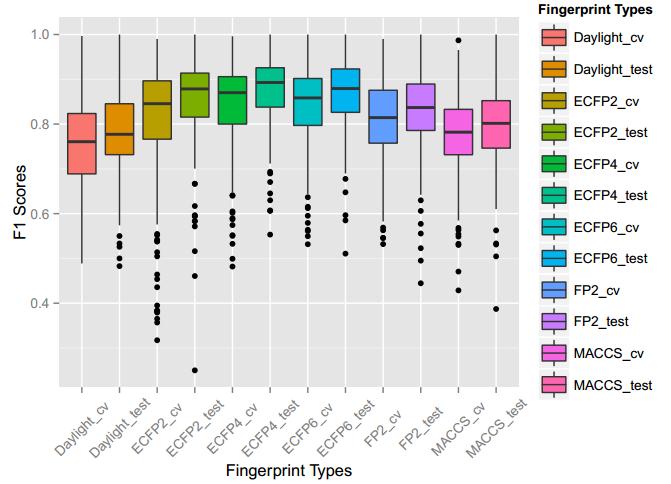
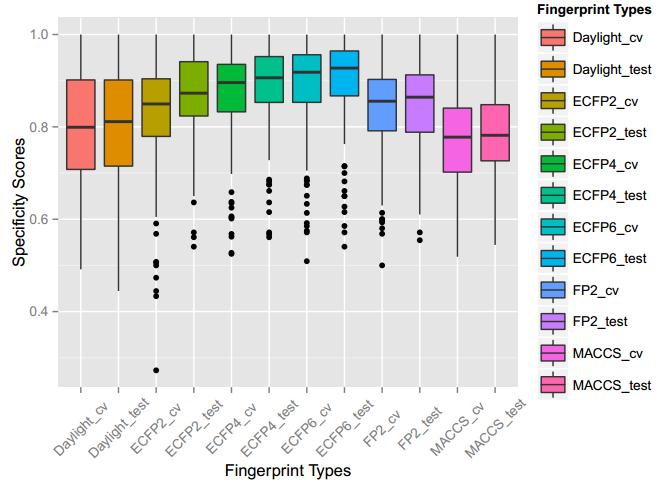
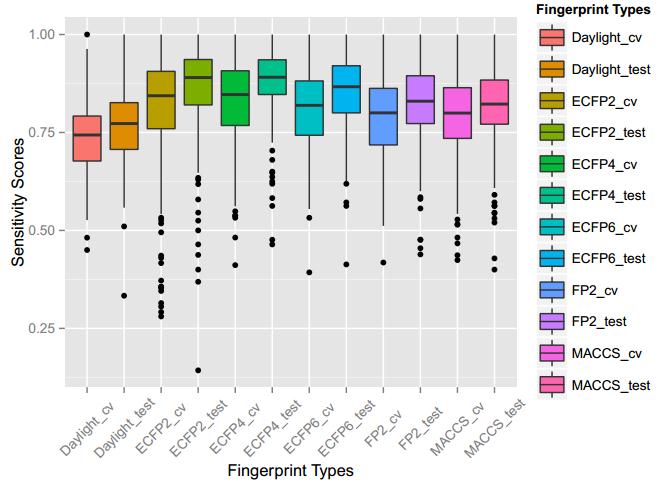
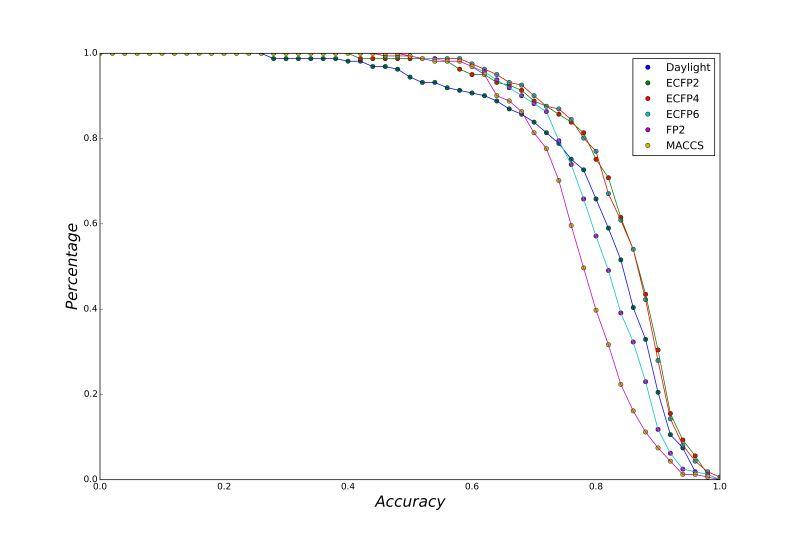
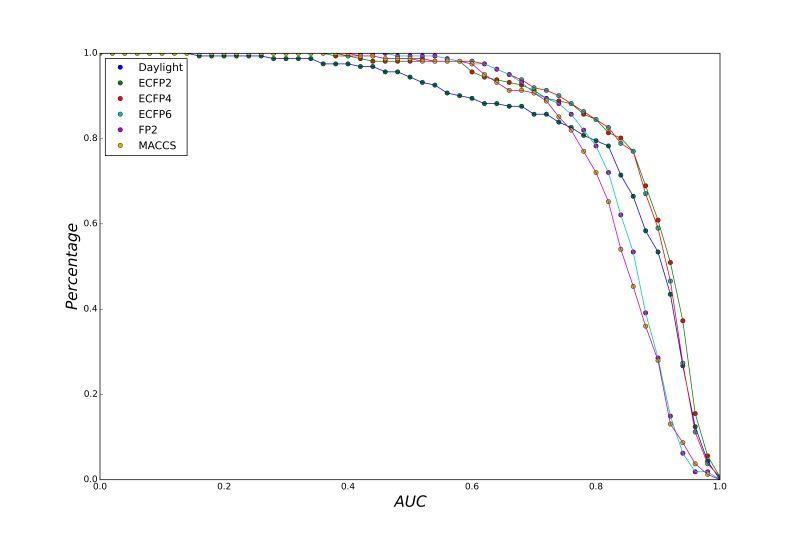
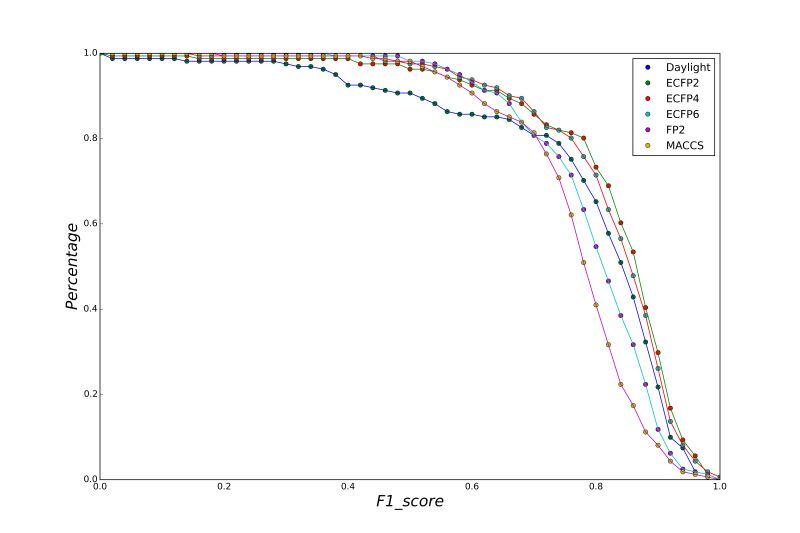
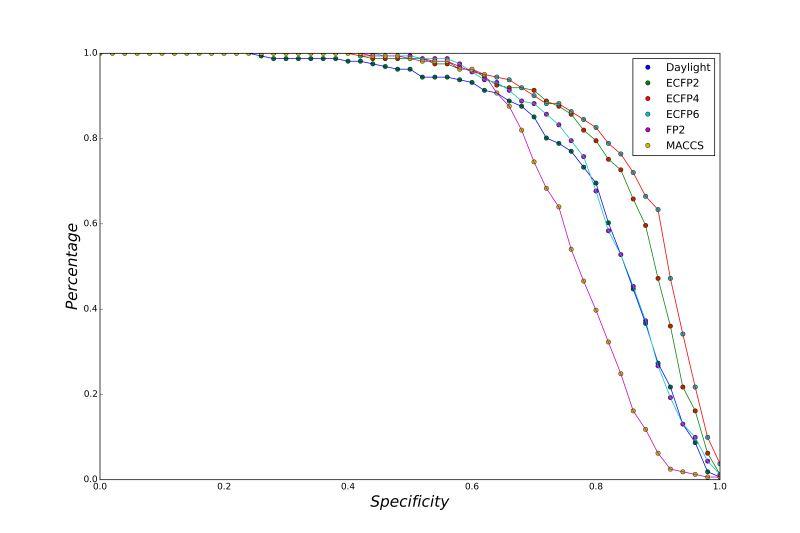
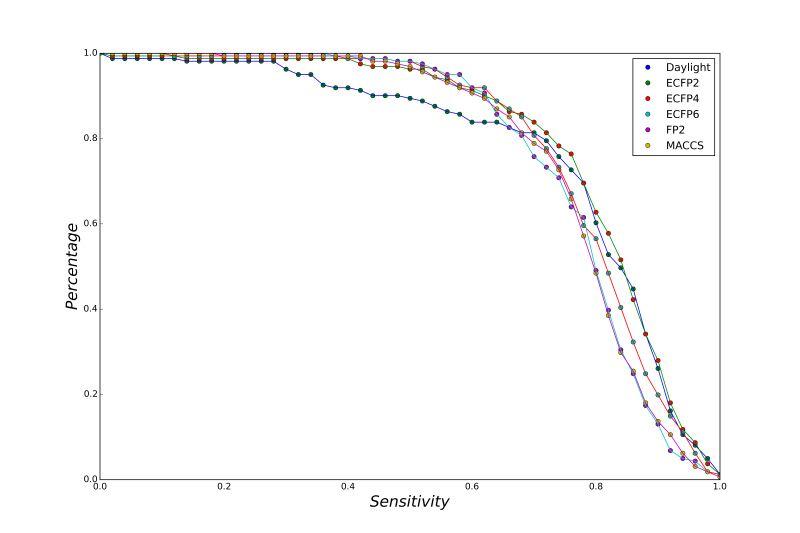
A series of high confidence QSAR models were built by Naïve Bayes and different fingerprint representations for 161 proteins. The Naïve Bayes method for predicting the associations between AD-related proteins and chemicals was chosen as it provided both good performance for noisy data sets and a high speed of calculation. Herein, to obtain the best model performance, we compared 6 types of molecular fingerprints when establishing the prediction models, including FP2, MACCS, Daylight, ECFP2-2048, ECFP4-2048, and ECFP6-2048. To obtain the better prediction ability, we also ensemble all fingerprint models to obtain the average output. For each model, we applied five-fold cross validation and external validation to evaluate the prediction performance of models. For 5-fold cross validation, the data set is split into 5 roughly equal-sized parts firstly, and then we fit the model to four parts of the data and calculate the error rate of the other part. The process is repeated 5 times so that every part can be predicted as a validation set. To observe the stability of models, we repeated the cross validation program 10 times to report standard deviations of each statistics. For the external validation, the data were split in two parts for the validation step: compounds were clustered and assigned a cluster number. Clusters with an odd number were assigned to the test set, and the clusters with an even number were assigned to the training set. Models were built with the training set, and the test set was scored. Finally, a model was built with all data and scored against itself – the training set and whole set should provide similar validation statistics. Statistics on the performance of the models were reported, including commonly used ones in classification schemes: accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, AUC, and F-score values. ROC provides an overall score and does not need to specify a cut-off for distinguishing active from inactive compounds. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve provides an indication of the ability of the model to prioritize active compounds over inactive compounds. The ROC curve is the plot of the true positive versus the false positive rate.

Results
ROC curves
click the links below to view all corresponding targets
Models using different types of fingerprints
| FP2 fingerprints | MACCS fingerprints | Daylight fingerprints |
| ECFP2 fingerprints | ECFP4 fingerprints | ECFP6 fingerprints |
The 161 targets
| Uniprot_ID | Protein | Details |
|---|---|---|
| O00519 | Fatty-acid amide hydrolase 1 | View |
| O14672 | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10 | View |
| O95263 | High affinity cAMP-specific and IBMX-insensitive 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 8B | View |
| P00488 | Coagulation factor XIII A chain | View |
| P00491 | Purine nucleoside phosphorylase | View |
| P00519 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 | View |
| P00747 | Plasminogen | View |
| P00749 | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator | View |
| P00750 | Tissue-type plasminogen activator | View |
| P00797 | Renin | View |
| P01275 | Glucagon | View |
| P01375 | Tumor necrosis factor | View |
| P02766 | Transthyretin | View |
| P03372 | Estrogen receptor | View |
| P03956 | Interstitial collagenase | View |
| P04035 | 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase | View |
| P04049 | RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase | View |
| P04062 | Glucosylceramidase | View |
| P04156 | Major prion protein | View |
| P04439 | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen, A-3 alpha chain | View |
| P04626 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | View |
| P04629 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | View |
| P04798 | Cytochrome P450 1A1 | View |
| P05067 | Amyloid beta A4 protein | View |
| P05091 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | View |
| P05093 | Steroid 17-alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase | View |
| P05121 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 | View |
| P05164 | Myeloperoxidase | View |
| P05230 | Fibroblast growth factor 1 | View |
| P05362 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 | View |
| P06213 | Insulin receptor | View |
| P06239 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | View |
| P06241 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | View |
| P06276 | Cholinesterase | View |
| P06493 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 | View |
| P07339 | Cathepsin D | View |
| P07384 | Calpain-1 catalytic subunit | View |
| P07550 | Beta-2 adrenergic receptor | View |
| P07858 | Cathepsin B | View |
| P08069 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | View |
| P08172 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 | View |
| P08183 | Multidrug resistance protein 1 | View |
| P08253 | 72 kDa type IV collagenase | View |
| P08254 | Stromelysin-1 | View |
| P08311 | Cathepsin G | View |
| P08473 | Neprilysin | View |
| P08908 | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A | View |
| P08913 | Alpha-2A adrenergic receptor | View |
| P09874 | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1 | View |
| P09917 | Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase | View |
| P10275 | Androgen receptor | View |
| P10635 | Cytochrome P450 2D6 | View |
| P11086 | Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase | View |
| P11229 | Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1 | View |
| P11274 | Breakpoint cluster region protein | View |
| P11473 | Vitamin D3 receptor | View |
| P11511 | Aromatase | View |
| P12821 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme | View |
| P13569 | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | View |
| P14174 | Macrophage migration inhibitory factor | View |
| P14324 | Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase | View |
| P14555 | Phospholipase A2, membrane associated | View |
| P14780 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 | View |
| P15559 | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 | View |
| P16050 | Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase | View |
| P16083 | Ribosyldihydronicotinamide dehydrogenase [quinone] | View |
| P16109 | P-selectin | View |
| P17612 | cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha | View |
| P17787 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit beta-2 | View |
| P18054 | Arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase, 12S-type | View |
| P19438 | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A | View |
| P19525 | Interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase | View |
| P21397 | Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] A | View |
| P21728 | D(1A) dopamine receptor | View |
| P21730 | C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 | View |
| P21917 | D(4) dopamine receptor | View |
| P22102 | Trifunctional purine biosynthetic protein adenosine-3 | View |
| P22303 | Acetylcholinesterase | View |
| P23219 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 | View |
| P23443 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase beta-1 | View |
| P24385 | G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 | View |
| P25025 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 2 | View |
| P25098 | Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 | View |
| P27338 | Amine oxidase [flavin-containing] B | View |
| P27695 | DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase | View |
| P27986 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha | View |
| P28223 | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A | View |
| P28335 | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2C | View |
| P28482 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 | View |
| P28845 | Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 1 | View |
| P29274 | Adenosine receptor A2a | View |
| P29466 | Caspase-1 | View |
| P29474 | Nitric oxide synthase, endothelial | View |
| P29475 | Nitric oxide synthase, brain | View |
| P30291 | Wee1-like protein kinase | View |
| P30556 | Type-1 angiotensin II receptor | View |
| P30926 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit beta-4 | View |
| P31645 | Sodium-dependent serotonin transporter | View |
| P31749 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | View |
| P32297 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-3 | View |
| P34972 | Cannabinoid receptor 2 | View |
| P34998 | Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 | View |
| P35228 | Nitric oxide synthase, inducible | View |
| P35354 | Prostaglandin G/H synthase 2 | View |
| P35462 | D(3) dopamine receptor | View |
| P35610 | Sterol O-acyltransferase 1 | View |
| P35869 | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor | View |
| P36544 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7 | View |
| P37231 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma | View |
| P39900 | Macrophage metalloelastase | View |
| P41231 | P2Y purinoceptor 2 | View |
| P42261 | Glutamate receptor 1 | View |
| P42262 | Glutamate receptor 2 | View |
| P42345 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR | View |
| P42574 | Caspase-3 | View |
| P43681 | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-4 | View |
| P48039 | Melatonin receptor type 1A | View |
| P48147 | Prolyl endopeptidase | View |
| P49682 | C-X-C chemokine receptor type 3 | View |
| P49768 | Presenilin-1 | View |
| P49810 | Presenilin-2 | View |
| P49840 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 alpha | View |
| P49841 | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta | View |
| P49862 | Kallikrein-7 | View |
| P50052 | Type-2 angiotensin II receptor | View |
| P50406 | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 6 | View |
| P51677 | C-C chemokine receptor type 3 | View |
| P51681 | C-C chemokine receptor type 5 | View |
| P52732 | Kinesin-like protein KIF11 | View |
| P55055 | Oxysterols receptor LXR-beta | View |
| P55210 | Caspase-7 | View |
| P55211 | Caspase-9 | View |
| P55212 | Caspase-6 | View |
| P56817 | Beta-secretase 1 | View |
| P78536 | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 17 | View |
| Q00535 | Cyclin-dependent-like kinase 5 | View |
| Q01959 | Sodium-dependent dopamine transporter | View |
| Q02750 | Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 | View |
| Q03181 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta | View |
| Q05586 | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 | View |
| Q07343 | cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B | View |
| Q07869 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha | View |
| Q13224 | Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2B | View |
| Q13526 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 | View |
| Q13627 | Dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A | View |
| Q13936 | Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C | View |
| Q14289 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 2-beta | View |
| Q14790 | Caspase-8 | View |
| Q15078 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator 1 | View |
| Q15303 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | View |
| Q16572 | Vesicular acetylcholine transporter | View |
| Q16620 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | View |
| Q16739 | Ceramide glucosyltransferase | View |
| Q5S007 | Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 | View |
| Q8WW43 | Gamma-secretase subunit APH-1B | View |
| Q92731 | Estrogen receptor beta | View |
| Q96EB6 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 | View |
| Q99720 | Sigma non-opioid intracellular receptor 1 | View |
| Q9NR96 | Toll-like receptor 9 | View |
| Q9NZ42 | Gamma-secretase subunit PEN-2 | View |
| Q9Y5Z0 | Beta-secretase 2 | View |